How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after, whether for professional photography, recreational flying, or even commercial applications. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and essential safety procedures. We’ll explore the different components of a drone, explain how they work together, and provide practical tips to help you become a confident and responsible drone pilot.
From understanding the fundamental controls – throttle, pitch, roll, and yaw – to mastering advanced techniques like flips and 360-degree rotations, we’ll break down each step of the process. We’ll also cover crucial safety considerations, legal regulations, and best practices for maintaining your drone, ensuring a long and productive flying experience. Get ready to take to the skies!
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight and functionality. This section details the function of key components and explores different battery types and popular drone models.
Drone Component Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the coordinated operation of several key components. These include the propellers, motors, flight controller, battery, GPS module, and camera.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate the thrust necessary for lift and maneuverability. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into rotational motion. Brushless motors are common in modern drones due to their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: This is the drone’s “brain,” responsible for processing data from various sensors and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute commands. It integrates inputs from the GPS, accelerometer, gyroscope, and barometer.
- Battery: Provides the power for all drone components. Flight time is directly dependent on the battery’s capacity and the drone’s power consumption.
- GPS Module: Allows the drone to determine its location and maintain its position relative to the ground (essential for features like Return-to-Home). Accuracy varies depending on the GPS module’s quality and the environmental conditions.
- Camera: Captures photos and videos. Camera quality varies significantly between drone models, impacting image resolution, field of view, and video frame rate.
Drone Battery Types and Flight Time
Drone batteries are typically Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries, known for their high energy density. Different factors influence flight time, including battery capacity (measured in mAh), drone weight, and flight style (aggressive maneuvers consume more power). Higher mAh ratings generally translate to longer flight times.
- LiPo Batteries: These are the most common type due to their high energy density and relatively lightweight nature. They require careful handling and storage to prevent damage or fire.
- Battery Capacity (mAh): A higher mAh rating indicates a greater energy storage capacity, leading to longer flight times. For example, a 5000mAh battery generally provides longer flight times than a 3000mAh battery.
- Voltage (V): The voltage of the battery determines the power output. Higher voltage batteries often provide more power for faster flight speeds and more demanding maneuvers.
Comparison of Popular Drone Models
The following table compares the features and specifications of three popular drone models. Note that specifications can vary based on the specific model version.
| Model | Battery Life (approx.) | Camera Specs | Max Flight Distance (approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DJI Mavic 3 | 46 minutes (with standard battery) | 24mm, 4/3 CMOS sensor, 20MP stills, 5.1K video | 15 km (with FCC compliance) |
| Autel EVO II Pro | 40 minutes (with standard battery) | 8K video, 48MP stills | 9 km (with FCC compliance) |
| Parrot Anafi USA | 25 minutes (with standard battery) | 4K HDR video, 21MP stills, 180° adjustable camera | 4 km (with FCC compliance) |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures

A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for safe and successful drone operation. This section details the steps involved in preparing your drone for flight, ensuring proper calibration, and understanding best practices.
Step-by-Step Pre-Flight Checklist
- Battery Check: Ensure the battery is fully charged and securely connected to the drone.
- Propeller Inspection: Visually inspect each propeller for damage or looseness. Replace any damaged propellers.
- GPS Signal Acquisition: Allow sufficient time for the drone to acquire a strong GPS signal before takeoff. This is crucial for accurate positioning and stability.
- Gimbal Calibration (if applicable): Calibrate the gimbal to ensure smooth camera movements.
- Controller Connection: Verify a stable connection between the drone and its remote controller.
- Visual Inspection: Perform a visual inspection of the drone for any visible damage or obstructions.
- Safety Check: Assess the surrounding environment for potential hazards (obstacles, people, animals).
Drone Calibration Best Practices
Proper calibration is crucial for optimal performance and safety. This typically involves calibrating the compass, IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), and GPS. Consult your drone’s manual for specific calibration procedures.
- Level Surface: Calibrate on a flat, level surface away from any magnetic interference.
- Clear Skies: Ensure clear skies for optimal GPS signal acquisition during calibration.
- Follow Instructions: Carefully follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration procedures.
Pre-Flight Procedure Flowchart
A flowchart visually represents the sequence of pre-flight checks. This ensures all steps are completed before attempting takeoff. (Note: A visual flowchart would be included here in a visual medium, but a textual representation is difficult to create effectively.)
Basic Drone Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding the basic controls is fundamental to operating a drone safely and effectively. This section covers the fundamental control inputs and basic flight maneuvers.
Basic Drone Controls
Most drones use four basic control inputs: throttle, pitch, roll, and yaw. These controls manipulate the drone’s movement in three-dimensional space.
- Throttle: Controls the drone’s altitude. Increasing throttle causes the drone to ascend, while decreasing throttle causes it to descend.
- Pitch: Controls the drone’s forward and backward movement. Pushing the control stick forward moves the drone forward, and pulling it back moves the drone backward.
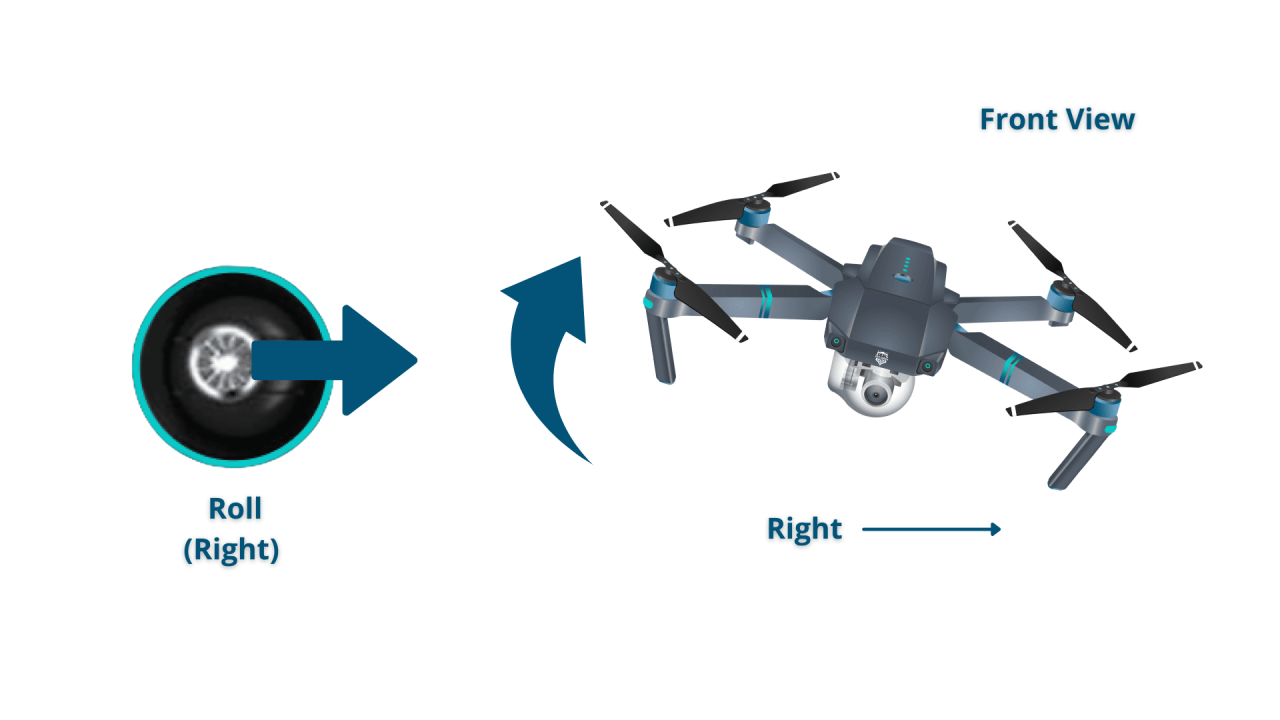
- Roll: Controls the drone’s left and right movement. Pushing the control stick to the right moves the drone to the right, and pushing it to the left moves the drone to the left.
- Yaw: Controls the drone’s rotation around its vertical axis (turning left or right).
Basic Drone Maneuvers
Mastering basic maneuvers is essential before attempting more complex flight operations. These include hovering, ascending, descending, and lateral movement.
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air without moving. This requires precise control of the throttle.
- Ascending: Increasing altitude by smoothly increasing the throttle.
- Descending: Decreasing altitude by smoothly decreasing the throttle.
- Lateral Movement: Moving the drone horizontally using the roll and pitch controls.
Techniques for Smooth and Controlled Movements
Smooth and controlled movements are achieved through practice and understanding the drone’s responsiveness. Avoid abrupt control inputs, which can lead to instability or loss of control.
- Small, Gradual Inputs: Use small, incremental adjustments to the control sticks.
- Anticipate Movement: Anticipate the drone’s response and adjust your inputs accordingly.
- Practice: Consistent practice is key to developing smooth and precise control.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Once comfortable with basic maneuvers, pilots can explore advanced techniques, different flight modes, and control methods. This section covers advanced maneuvers and control options.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers such as flips, rolls, and 360-degree rotations require precise control and a good understanding of the drone’s capabilities. These are generally enabled through specific flight modes.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Proper understanding of these aspects ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
- Flips: Rapid rotations around a single axis (e.g., forward flip, backward flip).
- Rolls: Rapid rotations around the drone’s longitudinal axis.
- 360-Degree Rotations: A complete rotation around the vertical axis.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to varying skill levels and flight situations. Beginner modes restrict maneuverability, while sport modes offer greater responsiveness and freedom of movement.
- Beginner Mode: Limits the drone’s speed and responsiveness, ideal for learning.
- Sport Mode: Allows for faster speeds and more aggressive maneuvers.
- GPS Mode: Utilizes GPS for precise position holding and automated features like Return-to-Home.
Drone Control Methods

Drones can be controlled using different methods, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages.
- Joystick Controller: Provides precise and responsive control, ideal for advanced maneuvers.
- Smartphone App: Offers a user-friendly interface, but may lack the precision of a dedicated controller.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Safe and responsible drone operation requires awareness of potential hazards and adherence to relevant regulations. This section Artikels safety measures and legal considerations.
Potential Hazards
Several hazards are associated with drone operation, including loss of control, battery failure, collisions, and damage to property or persons. Mitigating these risks is paramount.
- Loss of Control: Can be caused by various factors, including interference, battery failure, or pilot error.
- Battery Failure: LiPo batteries can malfunction if not handled properly, leading to unexpected power loss.
- Collisions: Collisions with obstacles or other objects can damage the drone and potentially cause injury.
Safety Measures
Implementing safety measures reduces the risk of accidents and ensures responsible drone operation.
- Visual Observers: Using visual observers can help maintain situational awareness.
- Emergency Landing Procedures: Knowing how to perform an emergency landing is crucial.
- Regular Maintenance: Regular maintenance keeps the drone in optimal condition.
- Weather Awareness: Avoid flying in adverse weather conditions.
Drone Regulations
Drone operation is subject to various regulations that vary by location. Familiarizing yourself with these regulations is crucial to avoid legal issues. Always check with your local aviation authority for the most up-to-date rules and regulations.
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning photos and videos. This section provides tips for capturing high-quality media and composing effective shots.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
High-quality aerial photography and videography requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques. Experimentation is key to mastering these skills.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, from pre-flight checks to maneuvering, is crucial for safe and effective operation. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including practical tips and troubleshooting, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Mastering these skills ensures responsible drone use and enjoyable flights.
- Resolution and Frame Rate: Select the appropriate resolution and frame rate based on your needs and storage capacity.
- Aperture and Shutter Speed: Adjust these settings to control depth of field and motion blur.
- ISO: Keep ISO as low as possible to minimize noise in your images.
- White Balance: Correctly setting white balance ensures accurate colors.
Camera Settings and Image Quality
Different camera settings influence image quality. Understanding their impact is crucial for achieving desired results.
- Resolution: Higher resolution results in larger file sizes but greater detail.
- Frame Rate: Higher frame rates produce smoother videos but require more storage space.
- Bitrate: Higher bitrate results in better video quality but larger file sizes.
Composing Shots
The unique perspective of a drone allows for creative shot composition. Utilize this to your advantage to create compelling visuals.
- Leading Lines: Use natural lines to guide the viewer’s eye through the scene.
- Rule of Thirds: Position key elements along the imaginary lines and intersections of a 3×3 grid.
- Unique Angles: Experiment with different camera angles to create dynamic and engaging shots.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition. This section Artikels a maintenance schedule and common troubleshooting steps.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule ensures your drone remains in top condition and minimizes the risk of malfunctions.
- Pre-flight Inspection: Inspect propellers, motors, and battery before each flight.
- Post-flight Cleaning: Clean the drone body and propellers after each flight.
- Battery Care: Store LiPo batteries properly to maintain their lifespan.
- Firmware Updates: Regularly check for and install firmware updates.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
This section provides a troubleshooting guide for common drone issues.
- Problem: Drone won’t power on. Solution: Check battery connection and charge level.
- Problem: GPS signal weak or unavailable. Solution: Fly in an open area with clear skies.
- Problem: Drone is unresponsive to controls. Solution: Check controller connection and battery levels.
- Problem: Propeller malfunction. Solution: Inspect and replace damaged propellers.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation. This section Artikels procedures for loss of control and other emergency situations.
Loss of Control Procedures
If you lose control of your drone, immediately attempt to regain control using the available controls. If unsuccessful, prioritize a safe landing.
- Attempt to Regain Control: Try adjusting the controls smoothly and methodically.
- Initiate Return-to-Home (if available): Use the Return-to-Home function to guide the drone back to its takeoff point.
- Emergency Landing: If Return-to-Home fails, prepare for an emergency landing in a safe location.
Emergency Landing
An emergency landing should be performed in a safe, open area, away from people, buildings, and obstacles. Gradually lower the drone’s altitude until it touches down gently.
Drone Malfunction Mid-Flight
If the drone malfunctions mid-flight, attempt to land it safely. If this isn’t possible, prioritize safety and let the drone land itself if possible. Always prioritize the safety of yourself and those around you.
Illustrative Examples of Drone Operation
This section provides examples of successful drone operation, showcasing the capabilities and versatility of drones.
Successful Drone Operation Scenario
Imagine a landscape photographer using a drone to capture stunning aerial shots of a mountain range. The photographer carefully plans the flight path, considering wind conditions and potential obstacles. They use a combination of manual control and automated features to achieve the desired shots. The mission is completed successfully, resulting in breathtaking images.
Drone Flight Path for Aerial Photography, How to operate a drone
For aerial photography of a coastline, the drone might follow a pre-planned path, moving along the shoreline at a consistent altitude. The camera would be angled slightly downward to capture the details of the coastline, the waves, and the surrounding landscape. This ensures a comprehensive and visually appealing set of images.
Different Perspectives Achievable with Drone Cameras
Drone cameras can capture a wide range of perspectives. Low-angle shots emphasize the scale of objects, while high-angle shots provide a broader context. Side angles can highlight details that would be missed from other viewpoints. The flexibility of drone cameras allows for creative and dynamic storytelling through visuals.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has provided a solid foundation in both, equipping you with the understanding and skills to operate a drone safely and confidently. Remember, responsible drone piloting is paramount. Always prioritize safety, adhere to regulations, and continue practicing to hone your skills. The world awaits exploration from above!
FAQ Compilation
What is the best type of drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with beginner modes are available. Look for models with features like GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functionality.
How often should I charge my drone battery?
It’s best to charge your drone battery after each flight. Avoid completely depleting the battery to maximize its lifespan.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If it doesn’t work, try to visually locate your drone and attempt a manual landing.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific regulations and procedures.
